
Scope of Microbiology. Chapter 1 Textbook: Foundations in Microbiology K.P. Talaro & A. Talaro. Microbiology . Definition- Greek- mikros- small; bios-life the branch of biology that studies microorganisms and their effects on humans.

damian-clements + Follow
Download PresentationAn Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.

The History and Scope of Microbiology I. Introduction to Microbiology Microbiology is the study of microorganisms usually less than 1mm in diameter which requires some form of magnification to be seen clearly Examples: Viruses Bacteria Fungi Algae Protozoans
1.35k views • 42 slides

DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY. DR.RITA SWAMINATHAN MR.NARAYANA KAMATH. PARASITOLOGY. INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLGY. DEFINITIONS.
1.62k views • 39 slides

History of Microbiology. History of Microbiology. Major contributions to the development of microbiology was the invention of the microscope by Anton von Leuwenhoek and the implementation of the scientific method. History of Microbiology.
865 views • 6 slides

History of Microbiology. Nature of Science Early Observations Spontaneous Generation Controversy Germ Theory of Disease. Nature of Science. Science is systematized knowledge developed through the application of the scientific method Scientific method Observations (objective vs. subjective)
827 views • 19 slides

History of Microbiology. 1. A history of Medicine2. A history of Science3. A history of Mankind. Living Things . Consist of one or more cells = cell is the basic unit of life Capture and use energy and raw materials = MetabolismSense and respond to the environment = AdaptationReproduce and grow = Sexual and asexual reproductionMaintain homeostasis imbalance in homeostasis is diseaseLiving organisms evolve.
654 views • 22 slides

The History and Scope of Microbiology. I. Introduction to Microbiology. Microbiology is the study of microorganisms usually less than 1mm in diameter which requires some form of magnification to be seen clearly Examples: Viruses Bacteria Fungi Algae Protozoans.
2.8k views • 42 slides

Methods of Microbiology. Staining Media Microscopy. Staining. Increase contrast of microorganisms Classified into types of stains Simple stain: one dye, one step Negative stain Positive stain Differential stain: distinguish one group from another Structural or special stains. Dyes.
765 views • 51 slides

History of Microbiology. Medical Microbiology Mrs. Bagwell. Scientific Revolution. Robert Hooke Englishman, mechanic and tinker C reated first working microscope First to observe dead cells Developed “ C ell Theory”. Cell Theory. The parts to the cell theory are as described below :
559 views • 15 slides

Scope and History of Microbiology. Why Study Microbiology 1 . Impact on Human Health 2. Balance of Nature - food source, play a role in decomposition, help other animals digest grass (cattle, sheep, termites).
1.4k views • 40 slides

1. Development of Microbiology History of Microbiology. Siti Sarah Jumali Room 3/14. Timeline. 1677 Observed "little animals" (Antony Leeuwenhoek) 1796 First scientific Small pox vaccination (Edward Jenner)
812 views • 12 slides

Fundamentals of Microbiology. Unit 1: 7 days. January 7 th : Intro to Microbiology. What are microbes? What do microbes do?. Microbes in our lives. Disease Spoiled food Food chain base Decomposers Digestion Vitamin synthesis Industrial synthesis of chemicals Food production
1.94k views • 156 slides
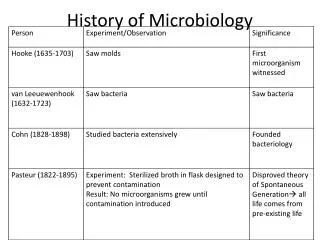
History of Microbiology. Domains of Life. Endosymbiotic Theory. Mitochondria and chloroplast have their own circular genome Also have 70S ribosomes This is evidence that organelles were originally bacteria taken up by a predatory eukaryote ancestor. Endosymbiotic Theory.
2.88k views • 128 slides

History of Microbiology. Chapter 1. Microbiology. The study of organisms too small to be seen individually with the naked eye during part or all of their life cycle. Types of Organisms. Scientific Nomenclature. Bacillus anthracis. Genus. Species. Why the Latin?.
392 views • 11 slides

History of Microbiology. Chapter 1. What is Microbiology ?. The study of organisms too small to be seen individually with the naked eye during part or all of their life cycle. Types of Microbes. Scientific Nomenclature. Bacillus anthracis. Genus. Species.
951 views • 31 slides

Microbiology of Water.
598 views • 21 slides